Bloom's Taxonomy
A review of Bloom’s Taxonomy and how to apply that to learning outcomes.

Bloom’s Taxonomy and the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy are ways of categorising and ordering thinking skills. They explain the process of learning and are thus a powerful tool for writing learning outcomes at a course level as well as at lower levels such as module, topics, class sessions, or assessment.
Bloom's Taxonomy
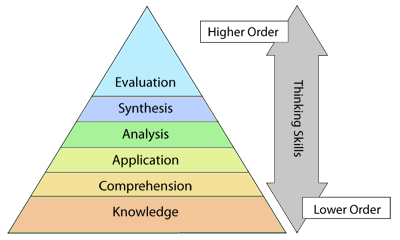
Bloom’s Taxonomy is a way of categorising and ordering thinking skills. It was initially introduced by Benjamin Bloom back in 1956. The purpose of this classification system is to classify and compare Lower Order Learning Skills from Higher Order Learning Skills. Below is a basic diagram of Bloom’s Taxonomy.
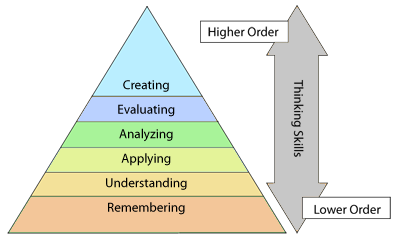
The Revised Bloom's Taxonomy
Anderson and Krathwhol are educators that built the revised version of Bloom’s taxonomy. The biggest change that occurred in the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy is that the classifications went from nouns to verbs. This helps remind us that learning is active and is not something that has already taken place. The other noticeable difference is the addition of ‘Creating’ as a higher order thinking skill. With the many additions of social media, web applications and educational technologies, students are now able to create at their fingertips. It is important to be aware of this and include it as a higher order learning skill.
Find out more about writing learning outcomes using Bloom’s Taxonomy or the Revised Bloom’s Taxonomy.
Bloom, B. S. (Ed.) (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The cognitive domain.
David McKay.
Miller, A. H., Bradford, W. I., & Cox, K. (1998). Student assessment in higher education: A handbook for assessing performance. Kogan Page Limited.

